
Graphs can either have positive correlation, negative correlation or no correlation. If data plotted on a scatter graph shows correlation, we cannot assume that the increase in one of the sets of data caused the increase or decrease in the other set of data – it might be coincidence or there may be some other cause that the two sets of data are related to. However, it is important to remember that correlation does not imply causation. On days with higher rainfall, there were a larger number of umbrellas sold. The graph shows that there is a positive correlation between the number of umbrellas sold and the amount of rainfall. The number of umbrellas sold and the amount of rainfall on 9 days is shown on the scatter graph and in the table.
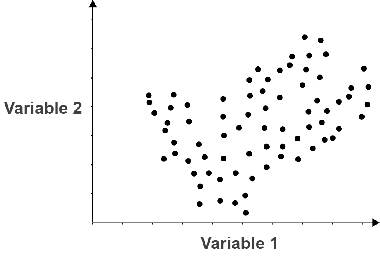
So, of these answer choices, we would say that negative 0.58 is the most likely value of the product-moment correlation coefficient for the given data set.Scatter graphs are a good way of displaying two sets of data to see if there is a correlation, or connection. For this reason, of our two answer options (B) and (C), we’ll choose the one that is closer to a Pearson correlation coefficient of negative 0.5. This suggests that the correlation coefficient is not particularly close to negative one, neither is it particularly close to zero. As we look at the data shown in our given diagram, we can see that it’s neither extremely far away from the best fit line nor extremely close to it. The data points in the data set represented by a correlation coefficient of negative 0.9 are much more tightly clustered about the line of best fit compared with those in the other data set. As we consider this range of Pearson correlation coefficients, the difference between them comes down to how tightly clustered about the best fit line the data points in a data set are.įor example, if we looked at data sets represented by correlation coefficients of negative 0.9 and negative 0.2, then, respectively, they might look like this. These are both negative values, and we see that one is closer to the extreme value of negative one than the other. This leaves us with answer choices (B) and (C). And we also know that option (A), which suggests that there is no correlation between the 𝑥- and 𝑦-variables in our data set, isn’t a valid answer either. That means options (D) and (E) can’t be our final choice. Any positive correlation coefficients are out of consideration. Looking then at our five answer options, we can see that what we’ve learned so far eliminates several of them. But here we see there is indeed a negative or inverse correlation between 𝑥 and 𝑦. If the line of best fit had a positive slope to it, the opposite would be true. This tells us that the correlation coefficient for this set of data lies somewhere below zero. Clearly, there is an inverse or a negative correlation between the values of 𝑥 and the values of 𝑦 that is, as 𝑥 gets larger, 𝑦 gets smaller. Looking at the set of data in our diagram, if we were to draw a best fit line for this set of data, we might draw it in by hand like this. In between these values, there’s a correlation coefficient of zero suggesting that there is no correlation between the two variables and then all the possible values in between these values named so far.

A correlation coefficient of positive one means the same thing, but for a data set that follows a positively sloping best fit line. That is, all the points in the data set lie along the same line. A coefficient value of negative one would describe a downward-trending data set that perfectly follows the line of best fit. The correlation coefficient can take on values anywhere between negative one and one.Īnd actually, in both of these extreme cases, that coefficient value describes perfect correlation. And the whole idea is to use a single number, this coefficient, to describe how well one of the variables in the data set correlates with the other. Another name for this is the Pearson correlation coefficient. Data sets consisting of two variables are called bivariate, and such sets can be described quantitatively by what’s called a product-moment correlation coefficient. Looking at our graph, we see that it consists of data where each data point has an 𝑥- as well as a 𝑦-value. What is the most likely value of the product-moment correlation coefficient for the data shown in the diagram? (A) Zero, (B) negative 0.94, (C) negative 0.58, (D) 0.37, (E) 0.78.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
